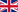
Publications in January 2011

Starting in a new year in January 2011 92 articles about chitosan and its derivates were published. The top themes in the last month were evaluation studies, studies in tissues and about nanoparticle with 26, 25 and 21 publications.
In that process China was with 25 articles
the country with the most publications about chitosan and its derivates. This was more than
twice the number of publications compared to the second active country in this field the USA
with 11 publications. Taiwan followed with 8 publications in January on the third rang. The
journals with the most published papers are listed in the table below.
| Journals |
Articles |
| Biomaterials | 8 |
| J Biomed Mater Res A | 6 |
| Acta Biomater | 5 |
| J Hazard Mater | 5 |
| Drug Delivery | 4 |
| J Biomater Sci Polym Ed | 4 |
| Int J Biol Macromol | 4 |
| Colloid Surf B Biointerfaces | 4 |
Table: Journalswith the most articles about chitosan and its derivates in January 2011
Three interesting papers of the publications from January from different fields are being introduced.
Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells at Low Silver Nanoparticle Concentrations using Chitosan Nanocarrier
Sanpui, Pallab, Chattopadhyay, Arun, Ghosh, Siddhartha Sankar, ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2011, PMID: 21280584 Related Articles
The authors developed chitosan nanocarrier for the delivery of silver nanoparticle into mammalian cells. Their aim was to induce apoptosis at very low concentrations of these nanoparticles. Sanpui et al. could determined that using these delivery system the concentration of Ag nanoparticles which were required to reduce the viability of HT 29 cells a human colon cancer cell line by 50 % was 0,33 μg/ml. This was much less than previous reported. The authors suggested that the induced apoptosis was a result of depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential. They could also demonstrate an increase of caspase 3 expression which indicated a participation of this caspases in the by Ag nanoparticles induced apoptosis.
An in situ formed biodegradable hydrogel for reconstruction of the corneal endothelium
PMID: 20832263 Related Articles, Authors: Liang, Ye, Liu, Wanshun, Han, Baoqin, Yang, Chaozhong, Ma, Qun, Song, Fulai, Bi, Qingqing, Journal: Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, Vol. 82 (1): 1-7, 2011
The authors of this paper developed an in situ formed hydrogel for reconstruction of corneal endothelium. For this hydrogel Liang et al. used a water soluble derivative of chitosan, hydroxypropyl chitosan (HPCTS) and sodium alginate dialdehyde (SAD). They could demonstrate that this composite hydrogel exhibit no toxicity and is biodegradable. Corneal endothelial cells which were encapsulated in this hydrogel showed a good survival.
Preparation and characterization of chitosan-grafted-poly(2-Amino-4,5-pentamethylene-thiophene-3-carboxylic acid N'-acryloyl-hydrazide) chelating resin for removal of Cu(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) metal ions from aqueous solutions
PMID: 21277322 Related Articles, Authors: Bekheit, M M, Nawar, N, Addison, A W, Abdel-Latif, D A, Monier, M, Journal: International journal of biological macromolecules, 2011
The authors copolymerize ethylacrylate as graft onto chitosan which was initiated by potassium persulphate and Moh´s salt in combination with a redox initiator system in limited aqueous medium. They try to modified the grafted chitosan by reacting of the ester group with 2-amino-4,5-pentamethylene-thiophene-3-carboxylic acid hydrazide which could eventually result in producing chitosan-grafted-poly(2-Amino-4,5-pentamethylene-thiophene-3-carboxylic acid N'-acryloyl-hydrazide) (chitosan-g-ATAH) chelating resin. Bekheit et al. studied the characteristics and the application of this modified resin for metal ion uptake. Therefore they used Cu(2+), Co(2+) and Ni(2+) ions.
Source: GoPubMed
chitosan, nanoparticles, cancer, nanocarrier
- Created on .