Chitosan

Due to their different degrees of deacetylation and molecular weights, chitosans are a large group of substances with different properties. In the following, we would like to introduce our product portfolio and show you the broad range of chitosan and its applications.
Read more about
- our quality lines
- origin of chitosan by HMC
- how to find the right chitosan?
- how to order?
- properties of chitosan
- applications of chitosan
- chitosan oligomer
Our quality lines
- Chitoscience® - for scientific research at universities
- Chitoceutical® - for medical technology and pharmceutical industry - this quality line is sudivided into 3 parts - suitable for the current status of your development
- Chitoceuticals® standard - applications in medical technology and first pharmaceutical research
- Chitoceuticals® GMP compliant - medical devices, applications of chitosan as excipient in pharmaceuticals
- Chitoceuticals® GMP - application of chitosan as API, usually derivatization of chitosan is performed - read more about costum manufacturing
Origin of chitosan by HMC
Generally, chitosan is obtained by the deacetylation of chitin. The chitin for HMC's chitosan comes mainly from Crustacea (Chionoecetes opilio). Other sources (e.g. shrimps, squid, mushrooms or insects) are also possible on
How to find the right chitosan?
Your chitosans are classified in different specifications. This enables you a precise selection and products with constant and reproducible properties. The names of our products consist of quality line, product name, degree of deacetylation and viscosity.
As example: "Chitoceuticals standard Chitosan 95/1500"
- Chitoceuticals standard - quality line
- Chitosan - product
- 95 - degree of acetylation 95%
- 1500 - Viscosity range 1500 mPas
Degree of deacetylation
The degree of deacetylation describes the amount of free amino groups of the molecule.
degree of deacetylation % = 100 - degree of acetylation %
The higher the degree of deacetylation, the more active is the molecule.
Viscosity
As standard, dynamic viscosity is measured as 1% solution in 1% acetic acid. Before measurement, the chitosan is dissolved by stirring for at least 2 hours. The viscosity also gives an indication of the molecular weight, but can not be directly converted.
How to order?
You can order our Chitoscience® and Chitoceuticals® standard products in our shop. For larger amounts or an offer please contact our
Properties of chitosan
The properties of chitosan can vary depending on the chitosan used. Chitosans are characterized by the following properties, for example:
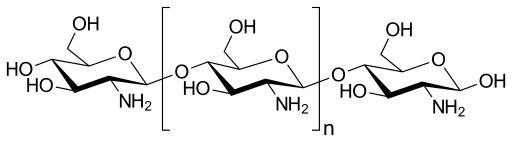
structural formula chitosan
- Molecular formula: (C8H11NO4)n
- CAS No.: 9012-76-4
- Molecular weight per unit: 161.15 g/mol
- Solubility
- soluble in nearly all diluted acids
- insoluble in sulfuric acid and water
- not thermo-elastic, decomposes at 280° C
- pKa 6.3
- high charge carrier density
- biodegradable
- non-toxic
- bacteriostatic
- fungistatic
- film and fiber forming, cross-linking
- immobilization of living organisms
- anti-inflammatory, improves wound healing
- stimulation of immune system and metabolism
- deodorizing
- bonding ability to proteins, heavy metals and aerosols
Examples for chitosan applications
-
Drug delivery systems in various forms such as microgranules, microspheres, hydrogels, nanoparticles or nanofibers for e.g. oral, transdermal, nasal or vaginal applications
-
non-viral vectors for the transport of nucleic acids such as RNA (e.g. for mRNA vaccines) or DNA drug enhancers of vaccines
-
Scaffold in the field of tissue engineering for the regeneration of e.g. heart muscle tissue, bones, skin, eyes or nerves
-
Wound dressings with haemostatic and antibacterial effects
Read more in our overview of scientific articles.
Chitosan Oligomer
Chitosan oligomer is a chitosan oligosaccharide that consists of β-(1➔ 4) linked D-glucosamine. It can be produced by deacetylation and hydrolysis starting from chitin.
Applications for Chitosan Oligomer
- Tissue engineering: chitosan oligomer promotes differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts – formation of bone tissue
- Drug delivery: vectors for gene delivery – chitosan oligomer forms complexes with plasmid DNA – drug delivery e.g. to lungs and intestinal epithelium
- Wound care: accelerated wound healing process, combination of chitosan and chitosan oligomers for wound dressings
- Antibacterial effects
- Antifungal effects in crops