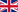
Publications in December 2011

Overall, 122 articles about chitosan were published worldwide in December 2011. China was the top publisher of the month again.
China: 32 articles
Indien: 9 articles
USA: 8 articles
| Top Journals | Publications |
| International Journal of Pharmaceutics | 8 |
| International Journal of Biological Macromolecules | 8 |
| Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces | 5 |
| Biomacromolecules | 5 |
| Journal of Material Science: Materials in Medicine | 5 |
Table: Journals with the most publications about chitosan and chitosan derivatives.
In the following three articles about vaccines will be introduced. One article is about sustained release vaccine delivery by using a chitosan hydrogel. Another article reports about chitosan as adjuvant for a norovirus vaccine. The third article introduces results in the filed of N-trimethylchitosan as nanocarrier for malaria vaccines. The latter is available as full text online. You can find the mentioned link at the end of this article.
Chitosan hydrogels containing liposomes and cubosomes as particulate sustained release vaccine delivery systems
Gordon S., Young K., Wilson R., Rizwan S., Kemp R., Rades T., Hook S., Journal of Liposome Research, 2011 Dec. 22. (Epub ahead of print)
Several studies gave attention to sustained release depot systems by focusing their potential to enhance the efficacy of subunit vaccines. Above all, this research is about immunogenicity enhancement of a sustained release vaccine. For this purpose a depot formulation was combined with a particulate antigen delivery system. Antigens are compounds on which antibodies can link themselves in a specific way. In most cases antigens are proteins like ovalbumin (OVA). In the immunology OVA is used to cause an allergic reaction.
In this study the sustained vaccine release was investigated in vivo in experimental mice. The formulation was based on a chitosan thermogel with cationic nanosized liposomes loaded with OVA and the immunopotentiator Quil A (QA).
Indeed, gel-incorporated liposomes indicated instability. Thus, further investigations with more solid lipidic particulate systems had to be arranged. The research group choose chitosan thermogels with cubosomes.
The potential of thermo sensitive systems is approved in this study. Additionally accented is the importance of property matching concerning physicochemical and immunological properties of the particulate system to that of the depot.
Source: US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health
Norovirus vaccine against experimental human Norwalk Virus illness
Atmar R. L., Bernstein D. I., Harro C. D., Al-Ibrahim M. S., Chen W. H., Ferreira J., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Opekun A. R., Richardson C., Mendelman P. M., The New England Journal of Medicine, 2011 Dec. 8., 365 (23): 2178-87
So far vaccines against norovirus diseases or rather infections are not available. For this reason a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, double-blind test was arranged. Research objects of intranasal delivered supplements which contained a virus like particle vaccine were:
- safety
- immunogenicity
- efficacy
Chitosan and monophosphoryl lipid A were attached as adjuvants.
Either vaccine or placebo was administered to 18 to 50 year old healthy adults. Afterwards the Norwalk virus was delivered to the test persons. Then the test persons were controlled regarding infections and gastroenteritis symptoms.
All in all there was a positive study result. The supplement defends disease and infection after challenge with a homologous virus.
Source: US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health
Preliminary charcterization of N-trimethylchitosan as a nonocarrier for malaria vaccine
Nnamani P. O., Scoles G., Kröl S., Universität von Nigeria, Journal of Vector Borne Diseases, 2011 Dec., 48(4):224-30
In case of an infectious mosquito bite in malaria endemic areas a prophylactic drug administration against malaria disease is recommended. This administration should support the immune defence.
Current problems of malaria treatment are the increasing resistance of morbiferous vermin against the approved Artemisinin combination therapies on the one hand and the feared cross-resistance to unrelated drugs on the other hand.
The goal is still to enhance the immunocompetence of humans living in malaria endemic areas.
For prophylaxis it’s important to achieve an as high and long-lasting immune response as possible.
In this preliminary study N-trimethylchitosan (TMC) nanoparticles synthesized from chitosan were prepared and characterized as adjuvants for possible vaccines.
The research showed that TMC has the desired antigen delivery qualities. At this point further research regarding biological activities of TMC is necessary.
Additional information
The research group based their TMC production on a chitosan with middle to high molecular weight (400 kDa) and a degree of deacetylation of >95%. You can order a chitosan with these properties in our web shop. The product name is Chitosan 95/1000 (product number 24707). For pharmaceutical research we recommend the product line Chitoceuticals.
The specification of the recommended chitosan is available for download. Just click here.
Source: US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health
Click here to get the full text of the article.
Source: GoPubMed
chitosan, hydrogels, vaccine, norovirus, malaria, liposomes, cubosomes