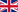
Publications in June 2011

70 articles were published in June, an obvious decrease of publications. For comparison, 84 articles were published in May. In June 2010 with 129 articles almost twice as much articles appeared, compared to this June.
China and the USA were again the strongest nations in terms of number of publications, followed by South Corea.
| Top Journals | Publications |
| Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces | 6 |
| Langmuir | 4 |
| Drug Dev Ind Pharm | 4 |
| Int J Biol Macromol | 4 |
| Biomacromolecules | 4 |
| Int J Pharm | 3 |
| Biomaterials | 3 |
Table: Journals with the most publications about chitosan and chitosan derivatives.
Below two publications of the sectors agriculture and medicine are shortly introduced.
Binding of heavy metal contaminants onto chitosans - An evaluation for remediation of metal contaminated soil and water
A. Kamari, I. D. Pulford, J. S. Hargreaves, Journal of environmental management, 2011
Chitosan characteristically binds heavy metals selectively. The positive binding efficiency of chitosan for argent (Ag(+)), cadmium (cd(2+)), copper (Cu(2+)), lead (Pb(2+)) and zinc (Zn(2+)) for example can be used for the reclamation of metal contaminated soil and water.
After evaluating the sorption behaviour the maximum sorption capacity was estimated as follows:
- 1.93 mmol/g Ag(+)
- 1.61 mmol/g Cu(2+)
- 0.94 mmol/g Zn(2+)
- 0.72 mmol/g Cd(2+)
- 0.64 mmol/g Pb(2+)
The main binding mechanism was the covalent interaction between metal ions and functional groups (amino and hydroxyl) of chitosans. Ion exchange was not an important process in this context.
Chitosans were able to bind metal ions on their surface, even at 11x dilution.
Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information
Antitumor activity and antioxidant role of a novel water-solube carboxymethyl chitosan-based copolymer
M. El-Far, M. Elshal, M. Refaat, I. M. El-Sherbiny, Drug development and industrial pharmacy, 2011
In this study, the natural polymer chitosan has been modified with a new simple and reproducible method to design a water-solube, nontoxic formulation that has been evaluated as a novel potential antitumor drug.
The antitumor activity was tested using mice with Ehrlich ascites tumor cells (EAC). The formulation was used in different doses dissolved in isotonic saline.
It has been found that the treatment significantly inhibits the growth of the tumor in depending on the used dose. Furthermore, the estimated hematological profil (hemoglobin, RBCs, WBCs) in EAC-bearing mice showed normal levels.
There are other biochemical assays that also show that the treatment in EAC-bearing mice has led to an increase of the antioxidant defense system without affecting lipid peroxidation.
Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information
Source: gopubmed
chitosan, agriculture, medicine, Heavy metals, antitumor
- Created on .