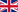
| Top Journals | Publications |
| Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces | 9 |
| International Journal of Biological Macromolecules | 9 |
| Acta Biomaterialia | 5 |
| Biomaterials | 5 |
Table: Journals with the most publications about chitosan and chitosan derivatives.
Source: GoPubMed
Two articles about chitosan nanoacarriers for drug delivery applications will be introduced below. Further articles and abstracts can be found on GoPubMed.
Chitosan-based drug nanocarriers: Where do we stand?
Garcia-Fuentes M., Alonso M. J., Journal of Controlled Release, 2012 March 23. (Epub ahead of print)
In the field of transmucosal nanometric drug delivery chitosan-based nanocarriers have already been extensively researched.
This great interest depends on various factors. Important factors are the simple and mild preparation technique as well as their property to bind macromolecules and facilitate their transport across mucosal barriers.
In this review the researchers introduce their contribution to the origin of chitosan nanocarriers in the mid 90s and summarize the early work that has impacted the development of this delivery technology. Furthermore, they show relevant application possibilities, e. g.:
- vaccinations
- transmucosal protein delivery and
- gene therapy.
In addition, the authors offer their perspective on the evident progress in the near future.
Source: National Center for Biotechnology Information
Erythrocytes load of low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles as a potential vascular drug delivery system.
Fan W., Yan W., Xu Z., Ni H., Colloids and Surface B: Biointerfaces, 2012 March 20. (Epub ahead of print)
Chitosan nanoparticles with low molecular weight (LMW) have already received considerable attention as colloidal drug carriers. (Colloids are cluster of particles with a size of 1 - 500 nm.)
But when LMW chitosan nanoparticles are applied to intravascular drug delivery, the RES (reticuloendothelial system) limits the circulation time and the target-specific drug release of the LMW chitosan nanoparticles as a result of RES cell activity. RES cells are a part of the immune system. Among other things they are important for the control and the elimination of foreign particles.
However, erythrocytes, known as red blood cells (RBCs) and responsible for oxygen transport, have a long circulation time in the blood. But sometimes they are not suitable for loading and releasing of drug directly.
Because of their complementing properties the combination of LMW chitosan nanoparticles and RBCs is a desirable strategy. Goal of the study was to develop such a multifunctional drug carrier.
LMW chitosan nanoparticles were prepared by ionic gelation technique and investigated with regard to their erythrocyte compatibility. Interactions between particles and RBCs were studied by confocal microscopy where a light microscope scans the supplement one by one. Therefore many pictures in different focal planes arise and a sharp 3D overall image can be designed.
Results:
- LMW chitosan nanoparticles show good compatibility with RBCs and
- they can be easily attached to the surface of the RBCs.
It can be concluded that this combination offers new opportunities in vascular drug delivery.
- Created on .